- The role of protein in weight loss and maintenance - (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002916523274274)
- Effects of Protein Supplementation on Performance and Recovery in Resistance and Endurance Training - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6142015/)
- Effect of Dietary Protein Content on Weight Gain, Energy Expenditure, and Body Composition During Overeating - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3777747/ )
- The Effects of High-Protein Diets on Kidney Health and Longevity - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7460905/)
- COOKING AND ITS EFFECT ON NUTRITION - (https://www.acsedu.co.uk/uploads/Food/Lesson%201%20and%20Assignment%201%20Sample%20Human%20Nutrition%20II.pdf )
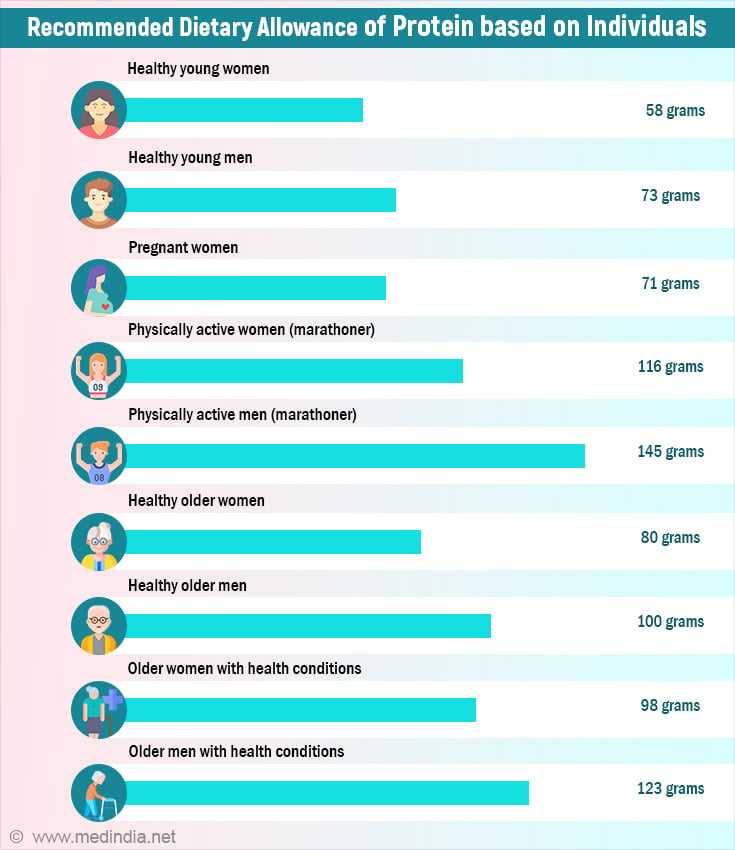
Daily Protein Requirement for Health
The daily protein requirement for health varies with individual but is generally around 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. For optimal muscle gain for active individuals, daily protein requirement is 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight.Typically recommending 10-35% of your daily calories from protein. For muscle gain, aim for higher protein intake tailored to your activity level.
Protein provides 4 calories per gram, contributing to your overall caloric intake. Balancing protein with other macronutrients is essential for effective weight management.
How to calculate protein intake?
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) suggests that adults consume around 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. To calculate the protein requirement:Formula: Daily Protein Requirement (grams) = Body Weight (kg) × 0.8
Why is Protein Important to our body?
Protein is an essential macronutrient (macronutrients provide energy and include fat and carbohydrates) that is used for the growth and repair of the body. Protein is an enzyme, that works as a carrier of signals from one part of the body to another and to form structures such as muscles. In short, proteins are like the bricks of a building. The body cannot store protein, it has to be taken in the diet.What is Complete and Incomplete Protein?
Complete protein food sources contain all the essential amino acids. The body cannot synthesize essential amino acids and hence must take them from the diet. Animal-based foods like meat, poultry, fish, milk, eggs, and cheese are some examples of complete protein sources.On the contrary, foods such as beans, lentils and soy products lack at least one of the essential amino acids and these are considered as sources of incomplete protein.
Good Sources of Protein:
- Lean Meats like Chicken breast, turkey, and lean cuts of beef or pork
- Fish and Seafood like Salmon, tuna, and shrimp
- Whole eggs
- Dairy Products such as Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and milk
- Legumes such as Beans, lentils, and chickpeas
- Nuts and Seeds such as Almonds, peanuts, chia seeds, and hemp seeds
- Whole Grains such as Quinoa, farro, and brown rice
- Plant-Based Proteins such as tofu and tempeh
Protein Deficiency
Protein Deficiency occurs when an individual does not consume enough protein to meet their body's needs. This condition can lead to various health issues, including:- Muscle Wasting
- Weakened Immune System
- Growth Issues
- Fluid retention in tissues
- Fatigue and Weakness
Protein for Bodybuilders
Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth; excessive intake is not always necessary for optimal results in bodybuilding. Bodybuilders who do not take extra protein put on muscle at the same rate as those who consume extra protein. It's important to balance protein with other macronutrients and overall caloric intake. In addition, high protein intake may put your kidney and liver at risk.Important Protein Facts
| ❖ | Approximately 18-20% of the body weight is due to proteins. |
| ❖ | The lifespan of proteins is only two days or less. |
| ❖ | Hair and nail are made up of a protein called keratin and these have sulphur bonds. More curly the hair the more sulphur links they have. |
| ❖ | Protein can provide about 10 to 35 percent of calories needed everyday. |
| ❖ | Plant proteins lack some of the essential amino acids but they may be healthier than animal-based protein as they contain less fat, no cholesterol, and plenty of dietary fiber. |
High Protein Intake | |
| ❖ | High protein intake in people with kidney disease may cause difficulty in eliminating all the waste products of protein metabolism. |
| ❖ | High-protein diet may have high fat content that increase your cholesterol level leading to heart disease, stroke and cancer. |
| ❖ | High-protein diet sometimes may replace carbohydrate intake leading to nutritional deficiencies and cause health problems like constipation. |
FAQs
1. How does protein help with weight loss?
Protein aids weight loss by increasing satiety, enhancing the Thermic Effect of Food (TEF), preserving lean muscle mass during weight loss, and promoting a balanced nutrient intake (1✔).
2. Can I get enough protein from a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Yes, with careful planning, vegetarians and vegans can meet their protein needs through a variety of plant-based sources, such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
3. What is the best time to consume protein for muscle recovery?
Consuming protein within 30 minutes to two hours after a workout can optimize muscle recovery and growth, but total daily intake is more important than timing (2✔).
4. Can consuming too much protein lead to weight gain?
Yes, excessive protein intake can contribute to weight gain if it leads to a caloric surplus, as any macronutrient can lead to weight gain if consumed in excess (3✔).
5. Are there any risks associated with high-protein diets?
High-protein diets can lead to potential risks such as dehydration, nutrient deficiencies, and increased strain on the kidneys and liver, especially in individuals with pre-existing conditions (4✔)
6. Is replacing meat with vegetables and grains effective for reducing protein intake?
Yes, replacing some meat with vegetables and grains effectively lowers protein intake while providing essential nutrients and fiber.
7. Do protein needs change with age?
Yes, protein needs may increase with age to help maintain muscle mass and strength, as older adults may require more protein to support muscle synthesis.
8. What are some high-protein snacks?
High-protein snacks include Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, hard-boiled eggs, protein bars, and nut butter with whole-grain crackers.
9. Does cooking affect protein content in food?
Cooking can affect the digestibility and availability of protein, but it generally does not significantly reduce the overall protein content of the food (5✔)
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email


























I want to learn how to be healthy.