What is Uterine Fibroid?
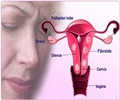
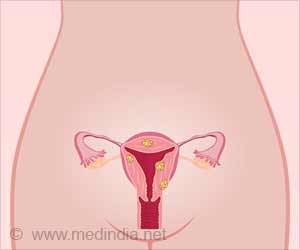
Uterine fibroids refer to benign tumors that arise from the muscles of the uterus. Other names for uterine fibroids include uterine leiomyoma, fibroleiomyoma, myoma and fibromyoma. Fibroids can occur as a single tumor or multiple tumors in the uterus. While some women with uterine fibroid remain asymptomatic, the usual symptom is severe pain and heavy bleeding during the menstrual cycle. The fibroids can press onto the bladder or the rectum causing frequent urination or rectal pressure (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Uterine fibroids
Go to source).
Other symptoms of uterine fibroids include enlargement of the lower abdomen (in case of large uterine fibroids), feeling of fullness in the pelvic area, lower back pain and pain during sex (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Uterine fibroids
Go to source).
Treatment for uterine fibroid includes surgical removal of the fibroid, hysterectomy, hormone therapy and embolization (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Uterine fibroids
Go to source).
Uterine Fibroids Health Facts
Statistics on Uterine Fibroid
- In the U.S, about 26 million women between the ages of 15 and 50 have uterine fibroids of a significant size. The presence of uterine fibroids is the most frequent indication for hysterectomy in menstruating women (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Management of Uterine Fibroids
Go to source).
Hormones and Uterine Fibroids
- Uterine fibroids are more common in women of childbearing age. It is due to the elevated levels of the hormones, estrogen and progesterone that feed the fibroids. The fibroids tend to shrink with the use of anti-hormone medication. When a woman reaches
menopause , they tend to shrink, or rarely disappear (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Uterine fibroids: When is treatment with hormones considered?
Go to source). - Higher production and circulation of estrogen have been found in obese women. Obese women are also found to have less serum hormone-binding globulin proteins that attach to sex hormones. This can result in more circulation of active estrogen. This raises risk of uterine fibroids in obese women (5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Association between obesity and the risk of uterine fibroids: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Go to source).
Types of Fibroids
- Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus. The presence of a fibroid does not indicate any form of cancer in the uterus.
- Fibroids are of three types, classified based on their location. Intramural fibroids lie within the muscle layer of the uterus; subserosal fibroids form on the outer surface of the uterus and submucosal fibroids are located just below the inner lining of the uterus. Some of the subserosal fibroids may develop a stem-base that supports the tumor; these are called pedunculated fibroids (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Uterine fibroids
Go to source).
Indication of Uterine Fibroid
- Although most women with fibroids do not present with any symptoms, abnormal uterine bleeding and excessive pain during the period are the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids (6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Contemporary Management of Fibroids in Pregnancy
Go to source).
Uterine Fibroids and Pregnancy
- Uterine fibroids and pregnancy can co-exist. The most common problems that occur in pregnant women with fibroids are placental abruption (early separation of the placenta), preterm delivery, breech presentation, necessity for Cesarean section, and failure of progression of a normal labor. Sometimes, women who have fibroids may go through a normal pregnancy and child-birth procedure (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Uterine fibroids
Go to source).
Studies on Uterine Fibroids Reason
- Some recent studies have shown that women who consumed dairy products like milk, cheese, ice cream, etc. are less likely to develop uterine fibroids than those who consumed fewer dairy products (7✔ ✔Trusted Source
A Prospective Study of Dairy Intake and Risk of Uterine Leiomyomata
Go to source).
Cure for Uterine Fibroids
- Untreated uterine fibroids may not disturb the daily activities of the woman. But they certainly require to be removed or to be closely watched for the rate of growth. If left on its own, the fibroid can grow to a size that can cause significant problems and be difficult to remove.
- Surgical procedures used to treat uterine fibroid include hysterectomy, endometrial ablation, uterine artery ligation, uterine artery embolization and myomectomy.