Glycemic Index (GI) Calculator is a tool that helps individuals assess the impact of various foods on blood sugar levels. Users can determine their GI values, aiding in the selection of low-glycemic foods for better blood sugar management and overall health.
GLYCEMIC INDEX (GI) is a measure, which helps in ranking carbohydrate rich foods, based on how they raise blood glucose levels within 2 - 3 hours of consumption of food. Foods are scored on a scale from 0 to 100, with pure glucose having a GI of 100.
The foods having a higher GI breaks down quickly and shoot up your blood sugar levels rapidly. The food having a lower GI takes a longer time to get digested and absorbed, resulting in more stable and gradual changes in blood sugar levels.
Glyemic Index Formula
Medindia’s Calculator uses an authentic formula to calculate the Glycemic Index :
GI = (area under the glucose response curve for test food) / (area under the glucose response curve for reference food) x 10.
The glycemic index (GI) is a concept that ranks the glycemic potency of foods (
1✔). It is calculated as the incremental area under the curve (iAUC) for blood glucose after consumption of a test food divided by the IAU of a reference food containing the same amount of carbohydrate.
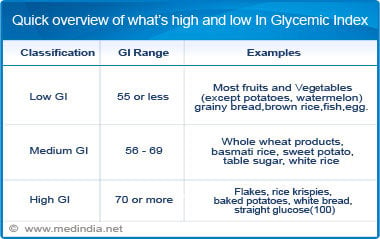
Glycemic Index Chart
A diet based on the glycemic index of the food is highly beneficial in diabetes management.Find out the GI of the common food using this application.
Factors Affecting Glycemic Index
Type of carbohydrate: Simple carbohydrates tend to have a higher GI than complex carbohydrates
Fiber content: High fiber foods tend to have a lower GI
Ripeness: Riper fruits usually have a higher GI
Cooking method: Cooking can increase GI (e.g., boiling vs. steaming)
Food processing: More processed foods often have a higher GI
Factors affecting the Glycemic Index of foods
Understanding Glycemic Index vs Glycemic Load
Glycemic Index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar.
Glycemic Load (GL) considers both the GI and the amount of carbohydrates in a serving, providing a more comprehensive view of a food’s impact on blood sugar.
Benefits of Low Glycemic Index Foods:
- Better Blood Sugar Control
- Weight Management
- Improved Heart Health
- Increased Satiety
- Reduced Inflammation
- Improved Digestion
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Health benefits of low glycaemic index foods, such as pulses, in diabetic patients and healthy individuals
How Can I Lower the Glycemic Index of My Meals?
8 principles of low-glycemic eating Choose Whole Grains: Opt for brown rice, quinoa, and whole grain bread.
Incorporate Fiber: Add vegetables, legumes, and fruits.
Pair Carbs with Protein and Fats: Combine with chicken, fish, or healthy fats.
Cook Al Dente: Keep pasta and vegetables firm.
Choose Low GI Fruits: Select berries, cherries, and apples.
Limit Processed Foods: Avoid those with added sugars.
Add Vinegar or Lemon Juice: Helps slow gastric emptying.
Plan Balanced Meals: Mix carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
FAQs
1. How does Glycemic Index affect heart health?
High GI foods can lead to spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels, which may increase the risk of heart disease over time.
2. What is the Glycemic Index for athletes?
Athletes may benefit from both low and high GI foods; low GI foods provide sustained energy, while high GI foods can aid in quick recovery after intense exercise.
3. Do cooking methods affect the Glycemic Index of food?
Yes, cooking methods can impact GI; for example, overcooking pasta can raise its GI, while cooking it al dente keeps it lower.
4. Are high Glycemic Index foods bad for everyone?
Not necessarily; while they can be less healthy for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes, they can be part of a balanced diet for others.
5. Can I eat high GI foods in moderation?
Yes, enjoying high GI foods in moderation can be fine, especially when balanced with low GI foods and a healthy lifestyle.
6. Are all whole grains low GI?
No, not all whole grains are low GI; some, like whole grain bread, can be moderate to high GI depending on processing.
7. Do low GI foods taste different?
Low GI foods can have a different taste and texture, often being more fibrous or less sweet compared to high GI options.
8. Can I measure GI at home?
Measuring GI at home is challenging; it typically requires controlled testing with blood glucose monitoring, usually done in a lab setting.
9. Is GI the only factor to consider for a healthy diet?
No, GI is one factor; overall nutrition, portion sizes, and the balance of macronutrients are also essential for a healthy diet.
10. Are there any risks to a low GI diet?
A low GI diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not well-planned; it's important to include a variety of foods to ensure balanced nutrition.
11. What are the best low glycemic foods?
The best low glycemic foods include non-starchy vegetables (like broccoli and spinach), whole grains (such as quinoa and barley), legumes (like lentils and chickpeas), nuts (such as almonds), and certain fruits (like berries and apples).
Recommended Readings on Glycemic Index
drug addiction. The food addict's quality of life can deteriorate physically, emotionally, socially or ...
Glycemic index and glycemic load tell you about the way in which food affects blood sugar and insulin. Take this quiz to find how well you know about the glycemic load diet to control your blood sugar ...
Jackfruit is not the first fruit you recall when you talk about healthy foods but its health benefits are plentiful and they are also great for diabetics.
Weight loss is a struggle for many individuals. This can be achieved simply by understanding the fullness factor, glycemic index and satiety index, which are all related to the hunger stimulus.
Carbohydrates in an athlete's diet provide energy and are vital to improve exercise performance. Find how out much carbohydrate an athlete needs to include in the diet for peak performance.
Diabetes has replaced every other condition to become the fastest growing lifestyle disease, globally. This disease also impacts children. Some people are more inclined to develop diabetes than others. Do you belong to the high- risk group? Spend 5 ...
The condition of excess glucose level in bloodstream can be regulated by a regular practice of yoga. Yoga helps to control blood sugar levels and promotes health in a person
Diabetes or diabetes mellitus, is an endocrine and metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time.
Insulin delivery devices have evolved drastically since their invention in 1922. They are all aimed to provide insulin to the patients with minimal discomfort.
The condition is not caused by a lack of insulin, but by the action of hormones produced during pregnancy that blocks the action of insulin.
The diabetic diet most often recommended is high in dietary fiber (especially soluble fiber) and nutrients, but low in fat (especially saturated fat) and moderate in calories.
Regular exercise especially in type II diabetes not only helps reduce the sugar but also reduces the demand for medication by 20% and helps you stay healthy.
Self-Monitoring Of Blood Glucose (SMBG) is recommended for the insulin-dependant and is desirable for all patients with diabetes
Self-Monitoring Of Blood Glucose (SMBG) is one of the greatest advancements in the management of Diabetes.
Encyclopedia section of medindia gives brief about glossary in diabetes
A comprehensive article on diabetes - both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, including : causes, signs, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, facts and a glossary on diabetes.
The blood sugar chart gives you the fasting glucose values and glucose tolerance test values for normal people and people with early diabetes and established diabetes. Also use the calculator to find out if you have diabetes.
Our easy to use blood sugar calculator helps you to get your blood sugar conversion results either in mg/dl used by the American system or in mmol/l used by the British system, which is accepted worldwide.
HbA1c calculator calculates average plasma and whole blood glucose levels. A1c test tells your average blood sugar level in the past 3 months and helps check whether your diabetes is in control.
Almost one-third of the people are unaware of the risk factors of diabetes. Find out if you run the risk of diabetes by using Diabetes Risk Assessment calculator.
GLYCEMIC INDEX (GI) is a scale which helps to rank carbohydrate- rich foods, depending on how they affect blood glucose levels, by comparing them to glucose.

















Why millet is showing high GI, it is low GI right?